总览
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void bar(int left, int top, int right, int bottom); |
画一个二维条形图 |
void bar3d(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int depth, int topflag); |
画一个三维条形图 |
int bdos(int dosfun, unsigned dosdx, unsigned dosal); |
DOS系统调用 |
int bdosptr(int dosfun, void *argument, unsigned dosal); |
DOS系统调用 |
int bioscom(int cmd, char abyte, int port); |
串行I/O通信 |
int biosdisk(int cmd, int drive, int head, int track, int sector, int nsects, void *buffer); |
软硬盘I/O |
int bioskey(int cmd); |
直接使用BIOS服务的键盘接口 |
int biosmemory(void); |
返回存储块大小,以K为单位 |
int biosprint(int cmd, int byte, int port); |
直接使用BIOS服务的打印机I/O |
long biostime(int cmd, long newtime); |
读取或设置BIOS时间 |
int brk(void *endds); |
用来改变分配给调用程序的数据段的空间数量 |
void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t *nelem, size_t width, int(*fcmp)(const void *, const *)); |
二分法搜索 |
1. bar
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void bar(int left, int top, int right, int bottom); |
画一个二维条形图 |
关注点: 绘制二维条形图需要左上角和右下角的坐标。 left 指定左上角的 X 坐标,top 指定左上角的 Y 坐标,right 指定右下角的 X 坐标,bottom 指定右下角的 Y 坐标。 当前填充图案和填充颜色用于填充条形图。 要更改填充图案和填充颜色,请使用 setfillstyle。
1.2 演示示例
1 |
|
1.3 运行结果

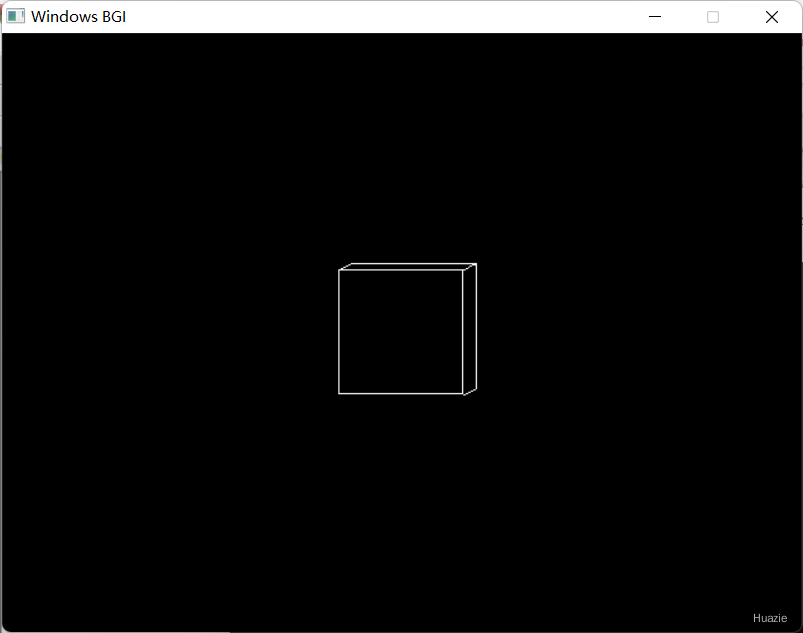
2. bar3d
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void bar3d(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int depth, int topflag); |
画一个三维条形图 |
关注点: 绘制三维条形图需要条形左上角和右下角的坐标。 left 指定左上角的 X 坐标,top 指定左上角的 Y 坐标,right 指定右下角的 X 坐标,bottom 指定右下角的 Y 坐标,depth 指定条的深度 以像素为单位,topflag 确定是否将 3 维顶部放置在条形图上(如果它不为零,则放置否则不放置)。 当前填充图案和填充颜色用于填充条形图。 要更改填充图案和填充颜色,请使用 setfillstyle。
2.2 演示示例
1 |
|
2.3 运行结果
3. bdos
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int bdos(int dosfun, unsigned dosdx, unsigned dosal); |
DOS系统调用 |
参数介绍:
int dosfun: 指定了要调用的DOS功能号。功能号决定了bdos函数要执行的具体DOS操作。例如,功能号0x09用于在屏幕上显示字符串,功能号0x3C用于创建或打开文件。unsigned dosdx: 用于传递额外的参数或数据给DOS功能。具体用途取决于所调用的DOS功能号,例如,在功能号0x09(显示字符串)中,dosdx通常指向包含要显示字符串的内存地址。unsigned dosal: 用于传递额外的参数或数据给DOS功能。与dosdx一样,它的具体用途取决于所调用的DOS功能号。例如,在文件操作中,dosal 可能用于指定文件的访问模式(如只读、写入等)。
3.2 演示示例
1 |
|
4. bdosptr
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int bdosptr(int dosfun, void *argument, unsigned dosal); |
DOS系统调用 |
参数介绍:
int dosfun: 指定了要调用的DOS功能号。void *argument: 一个指向任意类型数据的指针,通常用于传递额外的参数或数据给DOS功能。如果 dosfun 对应的功能是文件读取,那么 argument 可能指向一个包含文件名、文件缓冲区地址、读取字节数等信息的数据结构。unsigned dosal: 用于提供与 argument 相关的一些辅助信息,比如参数的长度或者其他特定于 dosfun 所调用功能的计数信息。
4.2 演示示例
1 |
|
5. bioscom
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int bioscom(int cmd, char abyte, int port); |
串行I/O通信 |
参数介绍:
int cmd: 指定了要执行的串行通信命令。常见的命令包括初始化串行端口、发送数据、接收数据、检查接收缓冲区是否有数据等。char abyte: 用于发送数据时指定要发送的字节。当执行发送数据的命令时,abyte 参数的值将被发送到指定的串行端口。int port: 指定了要使用的串行端口号。端口号通常是一个介于0到3之间的数字,对应于计算机上的COM1到COM4(或其他更高编号的端口,但这取决于计算机的硬件配置)。
5.2 演示示例
1 |
|
6. biosdisk
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int biosdisk(int cmd, int drive, int head, int track, int sector, int nsects, void *buffer); |
软硬盘I/O |
参数介绍:
int cmd: 要执行的磁盘操作命令。常见的命令包括读取磁盘扇区(通常是0x02)、写入磁盘扇区(通常是0x03)、检查磁盘扇区是否存在(可能是0x08或0x10,具体取决于BIOS版本)等。int drive: 指定了要访问的磁盘驱动器号。在大多数情况下,驱动器号是通过位移来表示的,其中0x00表示第一个硬盘(通常是C:),0x80表示第一个软盘驱动器(通常是A:),以此类推。int head: 指定了要访问的磁头号。在传统的磁盘驱动器中,每个磁道(track)都由一个或多个磁头来读写数据。磁头号的范围通常是从0到某个最大值(取决于磁盘的几何结构)。int track: 指定了要访问的磁道号。磁道号定义了磁盘上的圆周路径,数据就存储在这些路径上。磁道号的范围也是根据磁盘的几何结构来确定的。int sector: 指定了要访问的扇区号。每个磁道都被划分为多个扇区,每个扇区包含固定数量的字节(通常是512字节)。扇区号的范围取决于每个磁道的扇区数。int nsects: 指定了要连续读取或写入的扇区数。该参数允许一次性读取或写入多个扇区,从而提高了磁盘操作的效率。void *buffer: 用于存储读取的数据或提供要写入的数据。缓冲区的大小应该足够容纳指定数量的扇区数据(每个扇区通常是512字节)。在读取操作中,BIOS会将数据从磁盘传输到这个缓冲区中;在写入操作中,BIOS会从这个缓冲区中读取数据并写入到磁盘上。
6.2 演示示例
1 |
|
7. bioskey
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int bioskey(int cmd); |
直接使用BIOS服务的键盘接口 |
参数介绍:
int cmd: 指定要执行的键盘操作类型。0: 返回下一个在键盘键入的值【一个16位的二进制数】。函数将等待直到有键按下为止。当按下一个普通键时,低8位数存放该字符的ASCII码,高8位存放该键的扫描码。对于特殊键(如方向键、F1~F12等),低8位为0,高8位字节存放该键的扫描码。1: 检测是否有键按下。没有键按下时返回0。有键按下时返回按键码(任何按键码都不为0),但此时并不将检测到的按键码从键盘缓冲队列中清除。2: 返回Shift、Ctrl、Alt、ScrollLock、NumLock、CapsLock、Insert等控制键的状态。各键状态存放在返回值的低8位字节中。某位的值为1时,表示相应的键已被按过或相应的控制功能已打开;某位的值为0时,表示相应的键没被按过或相应的控制功能未打开。
7.2 演示示例
1 |
|
8. biosmemory
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int biosmemory(void); |
返回存储块大小,以K为单位 |
8.2 演示示例
1 |
|
9. biosprint
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int biosprint(int cmd, int byte, int port); |
直接使用BIOS服务的打印机I/O |
参数介绍:
int cmd: 指定要执行的打印机操作命令。0:向打印机输出一个字符。此时,byte 参数的值表示要输出的字符的 ASCII 码或汉字的内码。1:初始化打印机。这个命令通常用于设置打印机的初始状态或重置打印机。2:读取打印机的状态。函数返回值将表示当前打印机的状态,具体含义由返回值的位组合决定。
int byte: 当 cmd 为 0 时,byte 参数的值表示要输出到打印机的字符的 ASCII 码或汉字的内码。当 cmd 为 1 或 2 时,byte 参数的值可能不被使用或具有特定的含义(取决于 BIOS 的实现和打印机的类型),但在大多数情况下,可以将其设置为 0 或一个不影响操作的任意值。int port: 指定打印机并行口的编号。0:LPT1(第一个并行打印端口)1:LPT2(第二个并行打印端口)2:LPT3(第三个并行打印端口)- 以此类推,具体取决于计算机的配置和 BIOS 的支持。
返回值:
- 当 cmd 为 0 或 1 时,函数通常返回一个整数值,表示操作的结果或状态。返回值的具体含义可能因 BIOS 的实现和打印机的类型而异,但通常 0 表示成功,非 0 值表示错误或特定的状态信息。
- 当 cmd 为 2 时,函数返回一个整数值,该值的低 8 位有效,用于表示当前打印机的状态。例如,0x01 表示设备超时,0x08 表示输入/输出错误,0x40 表示认可,0x80 表示打印机不忙等。
9.2 演示示例
1 |
|
10. biostime
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
long biostime(int cmd, long newtime); |
读取或设置BIOS时间 |
参数介绍:
int cmd: 指定要执行的操作类型。0:读取计时器的当前值。此时,newtime 参数将被忽略,函数将返回从午夜开始(00:00)到当前时刻的计时器值,该值以时钟滴答声为单位。1:设置计时器的新值。此时,newtime 参数的值将被用作新的计时器值。请注意,直接设置计时器值可能会影响系统的正常计时功能,因此应谨慎使用此操作。
int newtime: 当 cmd 为 1 时,newtime 参数指定要设置的计时器新值。计时器值以时钟滴答声为单位。在大多数BIOS中,每秒的时钟滴答声频率约为18.2次(但具体值可能因计算机而异)。当 cmd 为 0 时,newtime 参数的值将被忽略。
10.2 演示示例
1 |
|
11. brk
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int brk(void *endds); |
用来改变分配给调用程序的数据段的空间数量 |
参数介绍:
void *endds: 指定新的数据段结束地址。
该函数可以将进程的数据段结束地址移动到该地址处,从而实现动态内存分配。如果传递的地址比当前数据段结束地址高,则数据段会向上扩展(即增加内存空间);如果传递的地址比当前数据段结束地址低,则数据段会向下收缩(即释放部分内存空间,但需要注意不要释放已在使用的内存,否则可能会导致程序崩溃)。
11.2 演示示例
1 |
|
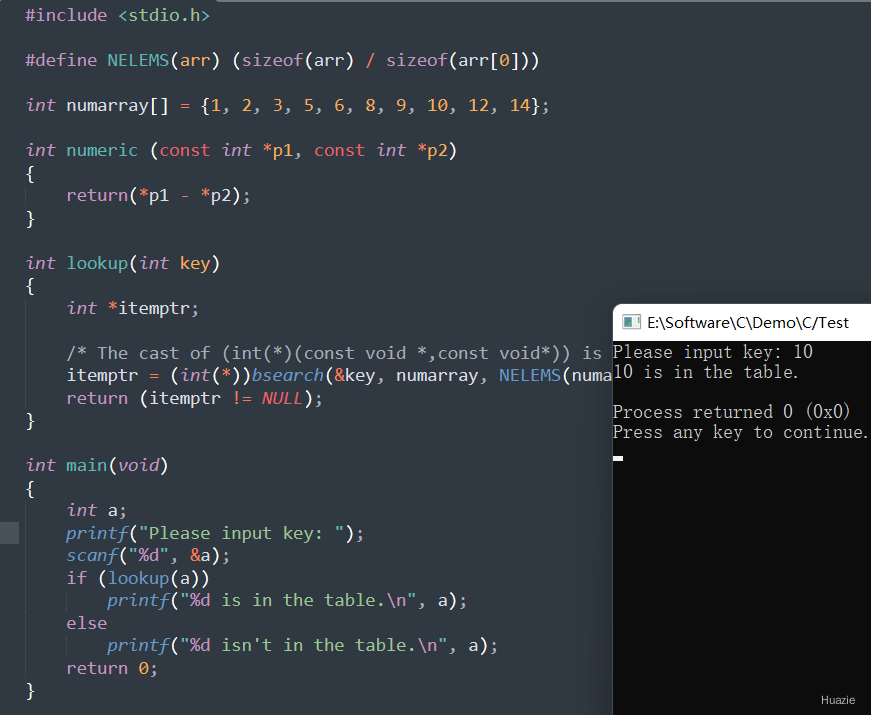
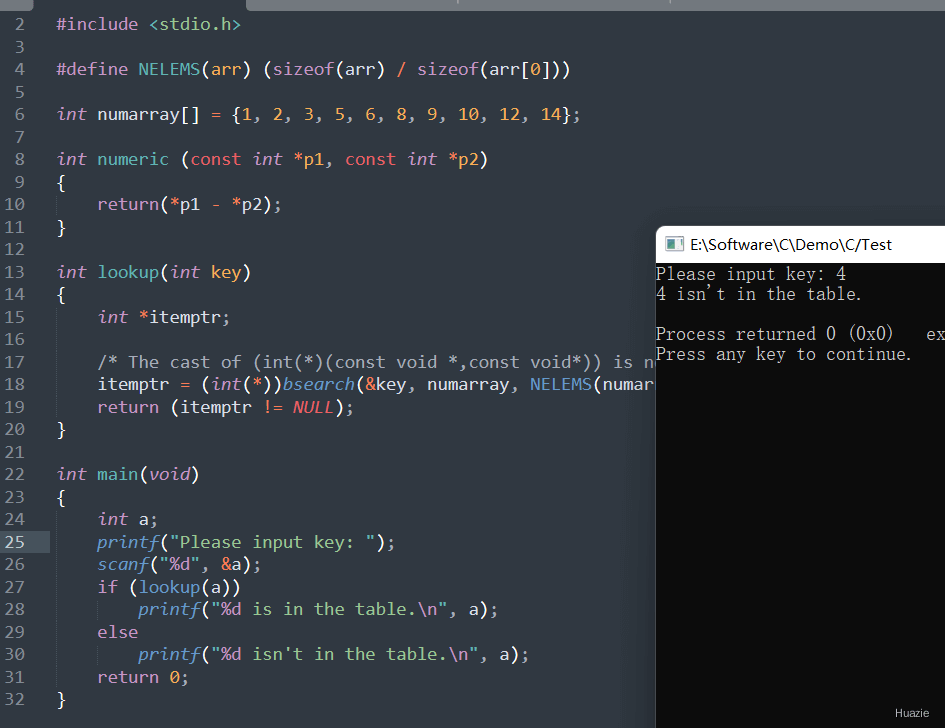
12. bsearch
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t *nelem, size_t width, int(*fcmp)(const void *, const *)); |
二分法搜索 |
参数介绍:
const void *key: 指向要搜索的元素的指针。key 指向的元素必须与 base 指向的数组中的元素具有相同的类型和大小。const void *base: 指向要搜索的数组的起始地址。数组中的元素必须已经按照某种顺序(通常是升序)排列好。size_t *nelem: 数组中元素的数量。size_t width: 数组中每个元素的大小(以字节为单位)。int(*fcmp)(const void *, const *): 指向比较函数的指针。比较函数的返回值如下:小于0:表示第一个元素小于第二个元素。等于0:表示两个元素相等。大于0:表示第一个元素大于第二个元素。
12.2 演示示例
1 |
|
12.3 运行结果