总览
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char * getmodename(int mode_name); |
获取指定的图形模式名 |
void getmoderange(int graphdriver, int *lomode, int *himode); |
获取给定图形驱动程序的模式范围 |
void getpalette(struct palettetype *palette); |
获取有关当前调色板的信息 |
int getpixel(int x, int y); |
获取得指定像素的颜色 |
char *gets(char *str); |
从标准输入流中读取字符串,直至遇到到换行符或EOF时停止,并将读取的结果存放在 buffer 指针所指向的字符数组中。 换行符不作为读取串的内容,读取的换行符被转换为 '\0' 空字符,并由此来结束字符串。 |
void gettextsettings(struct textsettingstype *textinfo); |
获取有关当前图形文本字体的信息 |
void getviewsettings(struct viewporttype *viewport); |
获取有关当前视区的信息 |
int getw(FILE *strem); |
从 stream 所指向文件读取下一个整数 |
int getx(void); |
获取当前图形位置的 x 坐标 |
int gety(void); |
获取当前图形位置的 y 坐标 |
struct tm *gmtime(long *clock); |
把日期和时间转换为格林尼治标准时间(GMT) |
void graphdefaults(void); |
将所有图形设置复位为它们的缺省值 |
char * grapherrormsg(int errorcode); |
返回一个错误信息串的指针 |
int graphresult(void); |
返回最后一次不成功的图形操作的错误代码 |
int getmaxwidth(void); |
获取屏幕的最大宽度 |
int getmaxheight(void); |
获取屏幕的最大高度 |
int getdisplaycolor( int color ); |
根据 color ,返回要显示的颜色值 |
int getwindowwidth(); |
获取图形界面窗口宽度 |
int getwindowheight(void); |
获取图形界面窗口高度 |
bool getrefreshingbgi(void); |
获取刷新基础图形界面标识 |
1. getmodename
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char * getmodename(int mode_name); |
获取指定的图形模式名 |
参数:
mode_name: 当前图形模式的模式代码。不同的图形模式对应不同的分辨率、颜色深度和显示模式。
1.2 演示示例
1 |
|
1.3 运行结果

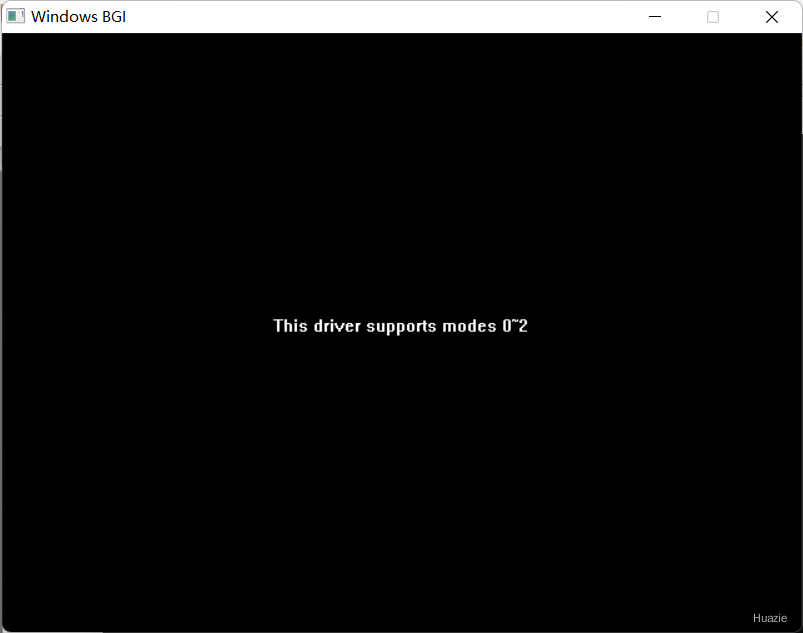
2. getmoderange
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void getmoderange(int graphdriver, int *lomode, int *himode); |
获取给定图形驱动程序的模式范围 |
参数:
graphdriver: 图形驱动程序的标识符。不同的图形驱动程序有不同的标识符,用于指定你希望使用的图形硬件或软件环境。例如,在某些图形库中,特定的数字或宏定义(如DETECT)可以用来自动检测可用的图形驱动程序。lomode: 一个指向整数的指针,用于接收指定图形驱动程序支持的最低显示模式编号。himode: 一个指向整数的指针,用于接收指定图形驱动程序支持的最高显示模式编号。
2.2 演示示例
1 |
|
2.3 运行结果
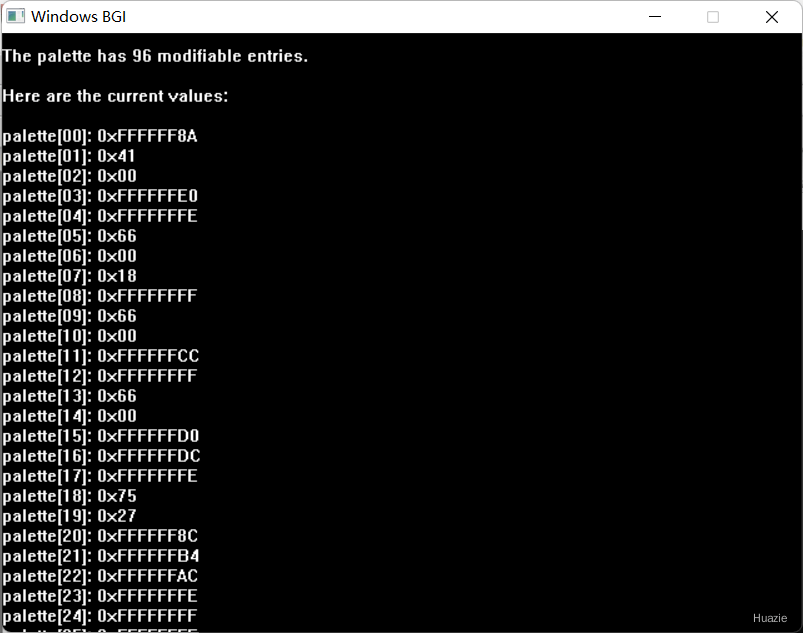
3. getpalette
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void getpalette(struct palettetype *palette); |
获取有关当前调色板的信息 |
参数:
palette: 一个指向palettetype结构体的指针。palettetype结构体通常包含了一系列元素,每个元素代表调色板中的一个颜色条目。在标准的图形库中(如Borland的BGI图形库),palettetype结构体可能包含多个unsigned char类型的成员,每个成员对应调色板中的一个颜色通道(如红色、绿色、蓝色),以及可能的其他信息(如亮度或透明度)。
注意: palettetype结构体的确切定义可能依赖于你使用的图形库。在某些实现中,它可能是一个简单的数组,每个元素代表一个颜色(可能是RGB值的一个组合),或者是一个更复杂的结构体,包含了关于每个颜色条目的更多信息。
3.2 演示示例
1 |
|
3.3 运行结果
4. getpixel
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getpixel(int x, int y); |
获取得指定像素的颜色 |
参数:
x: 想要获取的像素颜色值的点的横坐标。坐标原点(0, 0)通常位于屏幕的左上角。y: 想要获取的像素颜色值的点的纵坐标。
返回值:
函数返回一个整数,该整数代表指定坐标 (x, y) 上像素的颜色编码。颜色编码的具体含义取决于你使用的图形库和当前的图形设置。在某些图形库中,这个整数可能直接代表一个RGB颜色值,其中不同的位或字节表示红色、绿色和蓝色通道的强度。在其他情况下,这个整数可能是一个索引值,指向当前调色板中的一个颜色条目。
4.2 演示示例
1 |
|
4.3 运行结果
![]()
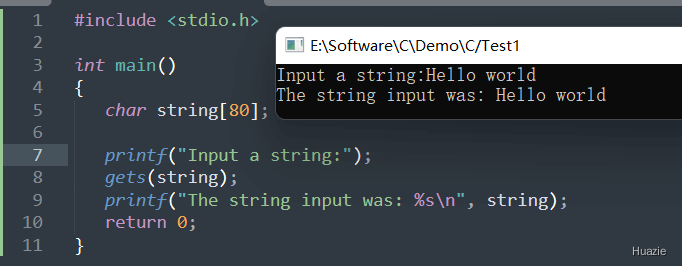
5. gets
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char *gets(char *str); |
从标准输入流中读取字符串,直至遇到到换行符或EOF时停止,并将读取的结果存放在 buffer 指针所指向的字符数组中。 换行符不作为读取串的内容,读取的换行符被转换为 '\0' 空字符,并由此来结束字符串。 |
注意: gets 函数可以无限读取,易发生溢出。如果溢出,多出来的字符将被写入到堆栈中,这就覆盖了堆栈原先的内容,破坏一个或多个不相关变量的值。
5.2 演示示例
1 |
|
5.3 运行结果
6. gettextsettings
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void gettextsettings(struct textsettingstype *textinfo); |
获取有关当前图形文本字体的信息 |
参数:
textinfo: 一个指向textsettingstype结构体的指针。该结构体用于存储当前的文本设置。textsettingstype结构体的具体定义取决于你使用的图形库。在不同的图形库中,这个结构体可能包含不同的成员,以反映该库支持的文本设置选项。
6.2 演示示例
1 |
|
6.3 运行结果
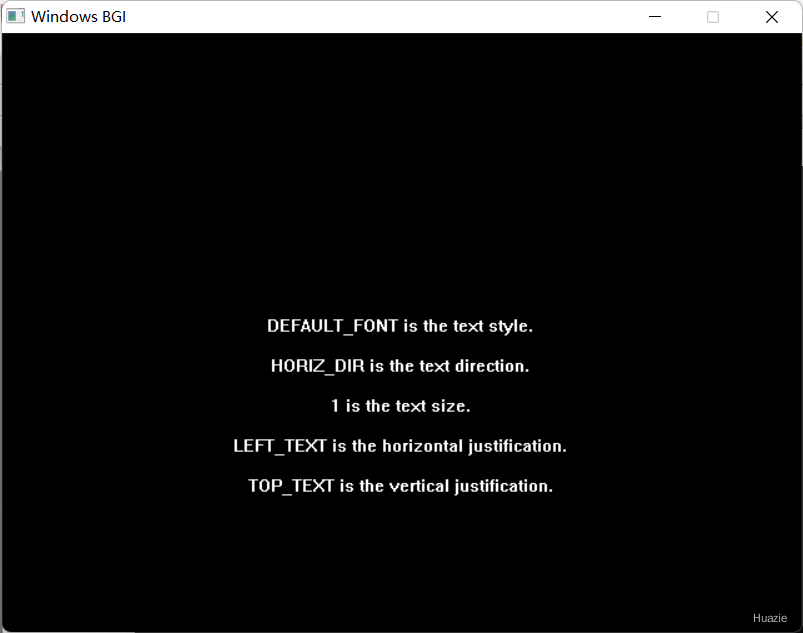
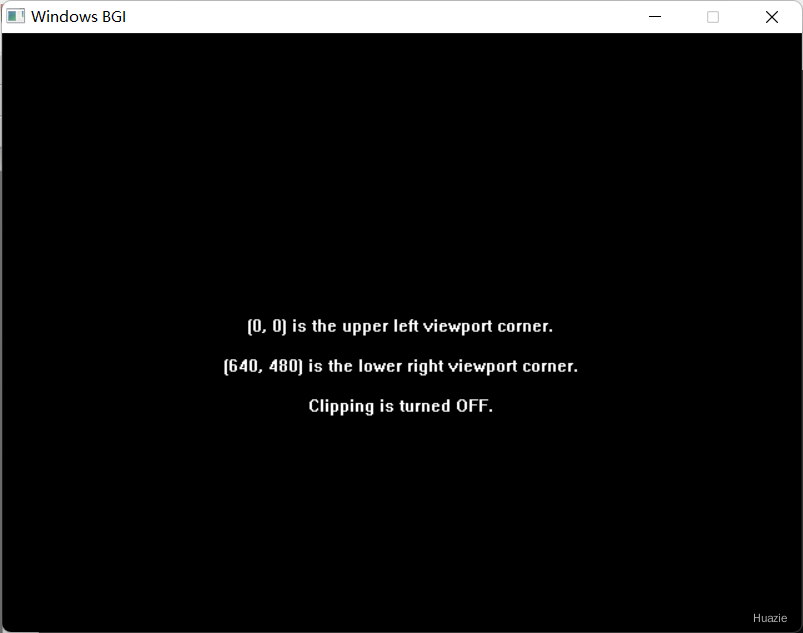
7. getviewsettings
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void getviewsettings(struct viewporttype *viewport); |
获取有关当前视区的信息 |
参数:
viewport: 一个指向viewporttype结构体的指针。该结构体用于存储当前的视口设置。调用getviewsettings函数后,这个结构体将被填充为当前的视口参数。viewporttype结构体的具体定义可能依赖于你使用的图形库,但通常它会包含以下成员:left, top: 这两个成员定义了视口的左上角坐标。坐标原点通常位于屏幕的左上角。right, bottom: 这两个成员定义了视口的右下角坐标。clip: 一个用于指示视口是否启用裁剪的标志。如果启用了裁剪,那么任何在视口之外的图形输出都将被忽略。
7.2 演示示例
1 |
|
7.3 运行结果
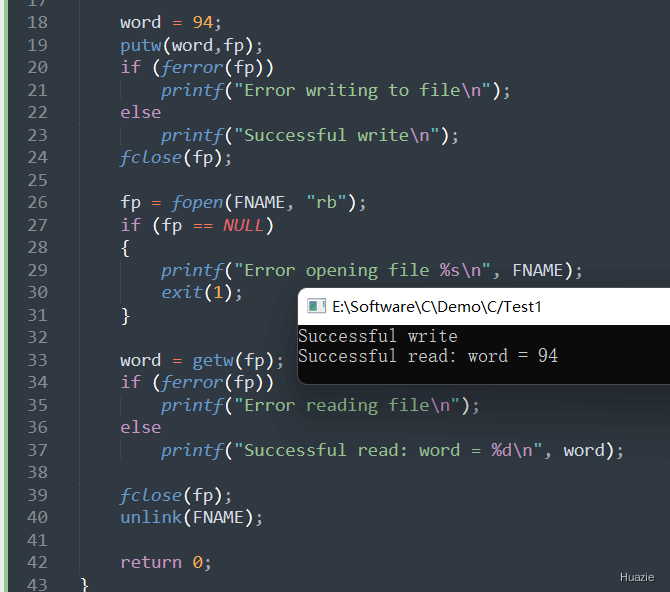
8. getw
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getw(FILE *strem); |
从 stream 所指向文件读取下一个整数 |
8.2 演示示例
1 |
|
8.3 运行结果
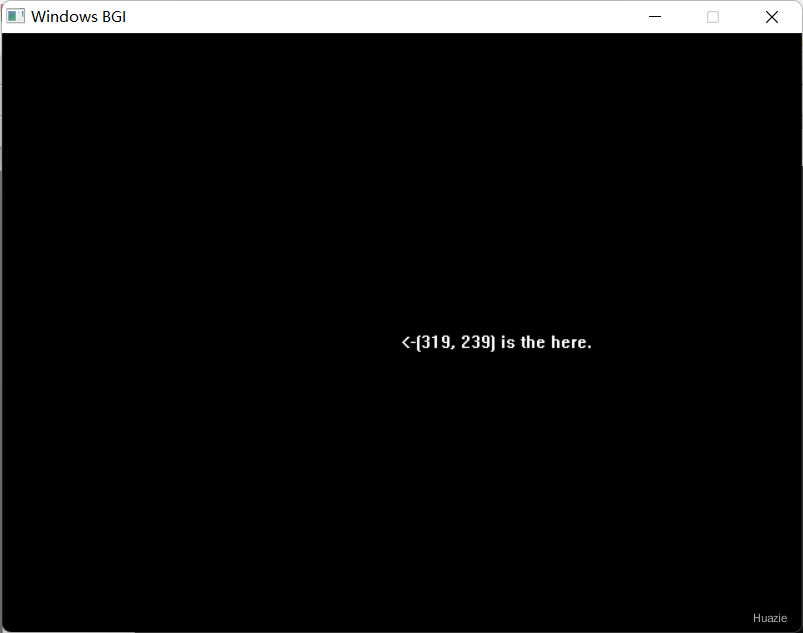
9. getx,gety
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getx(void); |
获取当前图形位置的 x 坐标 |
int gety(void); |
获取当前图形位置的 y 坐标 |
9.2 演示示例
1 |
|
9.3 运行结果
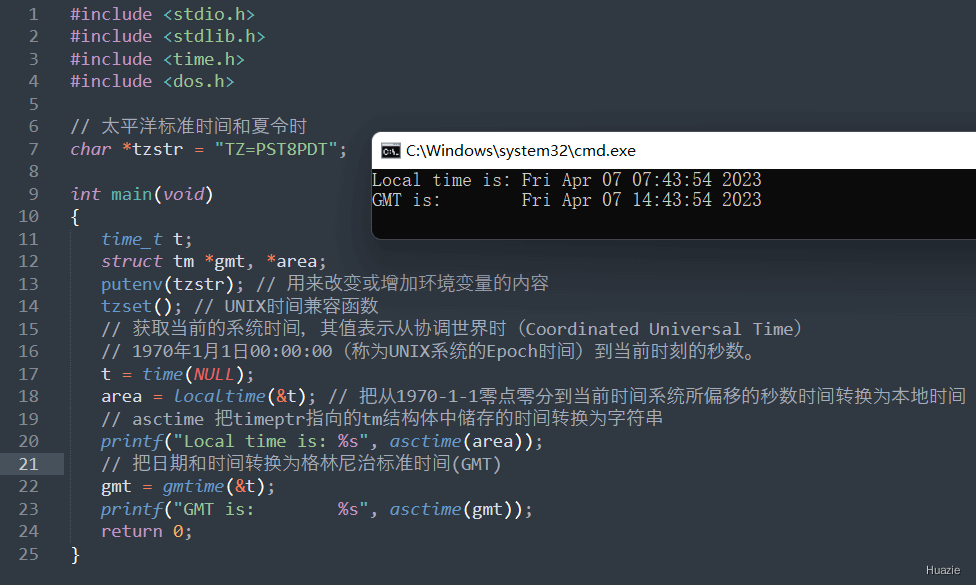
10. gmtime
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
struct tm *gmtime(long *clock); |
把日期和时间转换为格林尼治标准时间(GMT) |
10.2 演示示例
1 |
|
10.3 运行结果
11. graphdefaults
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void graphdefaults(void); |
将所有图形设置复位为它们的缺省值 |
11.2 演示示例
1 |
|
11.3 运行结果

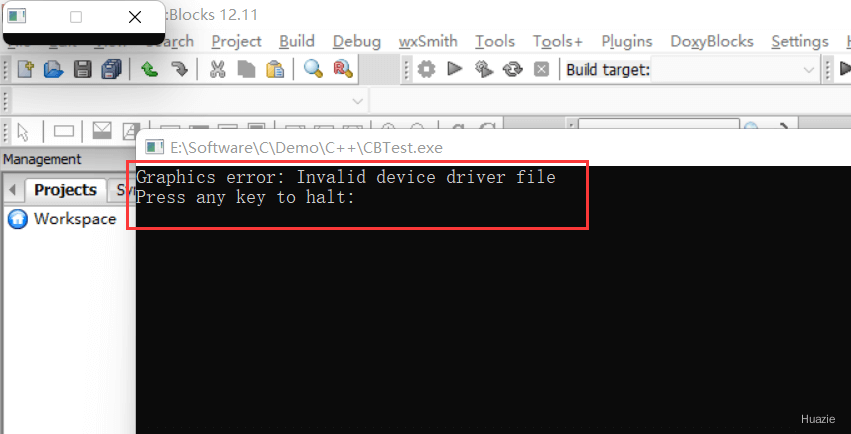
12. grapherrormsg
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char * grapherrormsg(int errorcode); |
返回一个错误信息串的指针 |
12.2 演示示例
1 |
|
12.3 运行结果
13. graphresult
13.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int graphresult(void); |
返回最后一次不成功的图形操作的错误代码 |
13.2 演示示例
1 |
|
13.3 运行结果

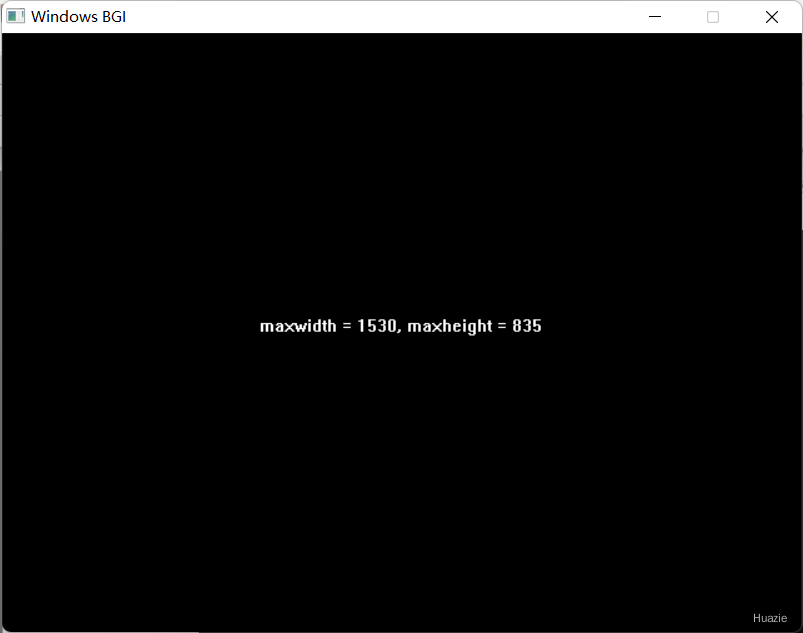
14. getmaxwidth,getmaxheight
14.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getmaxwidth(void); |
获取屏幕的最大宽度 |
int getmaxheight(void); |
获取屏幕的最大高度 |
14.2 演示示例
1 |
|
14.3 运行结果
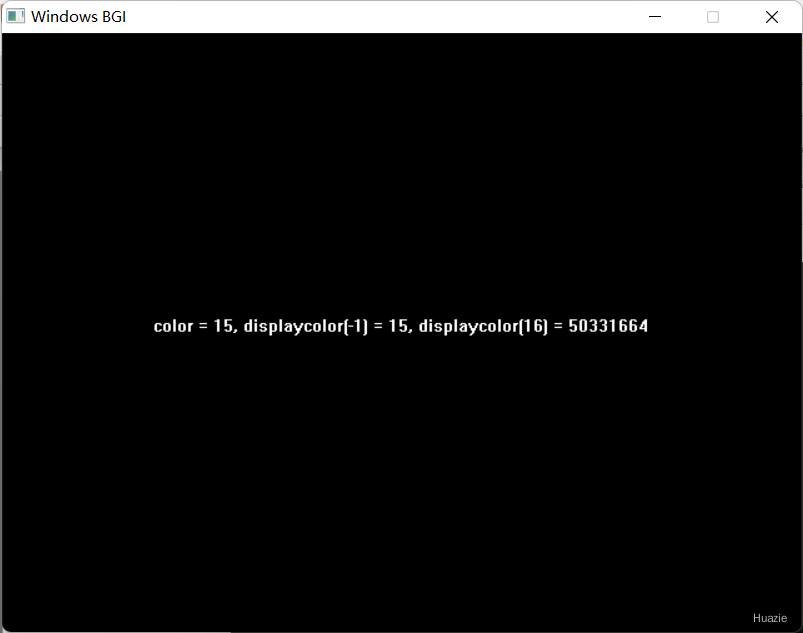
15. getdisplaycolor
15.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getdisplaycolor( int color ); |
根据 color ,返回要显示的颜色值 |
注意: color = -1 , 则返回 WHITE = 15 的颜色值;color < - 1 或 color > 15,则输出一个8位整数。
15.2 演示示例
1 |
|
15.3 运行结果
16. getwindowwidth,getwindowheight
16.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int getwindowwidth(void); |
获取图形界面窗口宽度 |
int getwindowheight(void); |
获取图形界面窗口高度 |
16.2 演示示例
1 |
|
16.3 运行结果
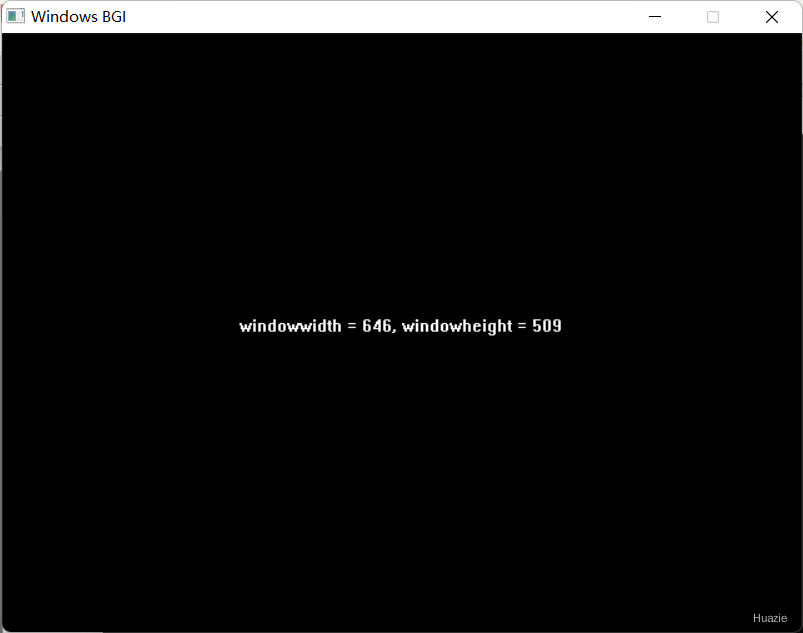
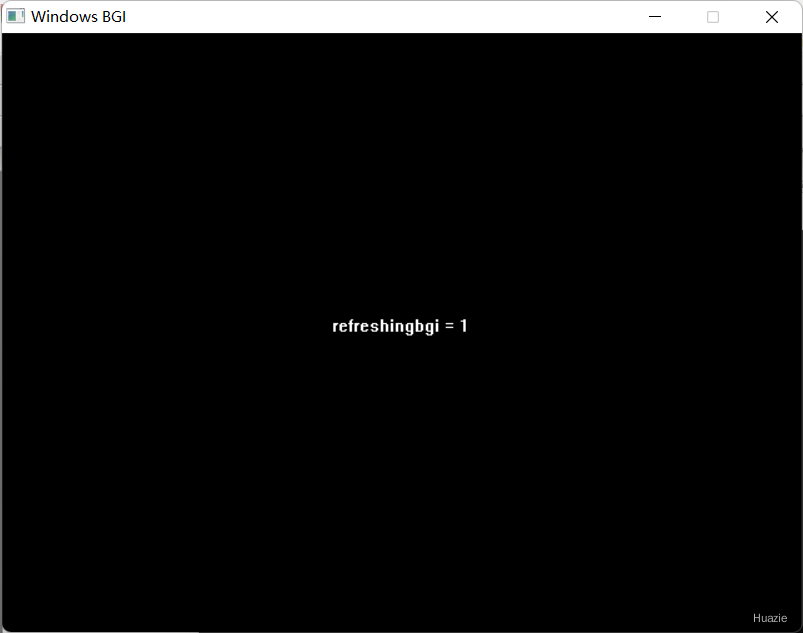
17. getrefreshingbgi
17.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
bool getrefreshingbgi(void); |
获取刷新基础图形界面标识 |
17.2 演示示例
1 |
|
17.3 运行结果