总览
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
unsigned imagesize(int left, int top, int right, int bottom); |
获取保存位图像所需的字节数 |
void initgraph( int *graphdriver, int *graphmode, char *pathtodriver ); |
初始化图形系统 |
int inport(int protid); |
从硬件端口中输入 |
void insline(void); |
在文本窗口中插入一个空行 |
int installuserdriver(char *name, int (*detect)(void)); |
安装设备驱动程序到BGI设备驱动程序表中 |
int installuserfont( char *name ); |
安装未嵌入BGI系统的字体文件(CHR) |
int int86(int intr_num, union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs); |
通用8086软中断接口 |
int int86x(int intr_num, union REGS *insegs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs); |
通用8086软中断接口 |
int intdos(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs); |
通用DOS接口 |
int intdosx(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs); |
通用DOS中断接口 |
void intr(int intr_num, struct REGPACK *preg); |
改变软中断接口 |
int ioctl(int fd, int cmd, ...) ; |
控制 I/O 设备 |
int isatty(int handle); |
检查设备类型 |
int ilogb (double x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(double) |
int ilogbf (float x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(float) |
int ilogbl (long double x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(long double) |
int isalnum(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为字母或数字 |
int isalpha(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为(大写或小写)字母 |
int isdigit(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为数字(0 - 9) |
int isinf(double x); |
检查浮点数 x 是否为无穷大(正无穷或负无穷) |
int isnan(double x); |
检查浮点数 x 是否为非数字(NaN) |
int isspace(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为空白字符,如空格(’ ‘)、制表符(’\t’)、换行符(’\n’)等。 |
char * itoa(int value, char *string, int radix); |
把一整数转换为字符串 |
1. imagesize
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
unsigned imagesize(int left, int top, int right, int bottom); |
获取保存位图像所需的字节数 |
参数:
left:矩形区域左边界的 x 坐标(水平方向起始位置)。top:矩形区域上边界的 y 坐标(垂直方向起始位置)。right:矩形区域右边界的 x 坐标(水平方向结束位置,需满足 right >= left)。bottom:矩形区域下边界的 y 坐标(垂直方向结束位置,需满足 bottom >= top)。
1.2 演示示例
1 |
|
上述代码利用图形库实现了一个在屏幕上移动箭头图形的动画效果。
1.3 运行结果
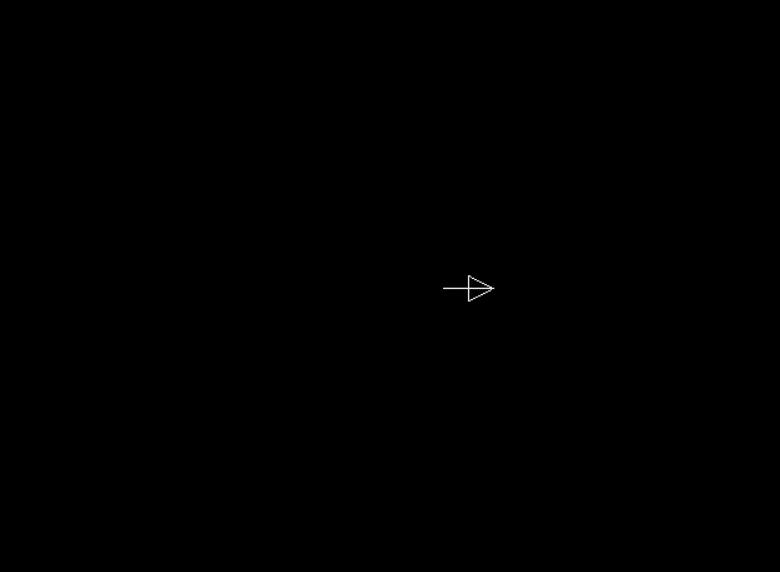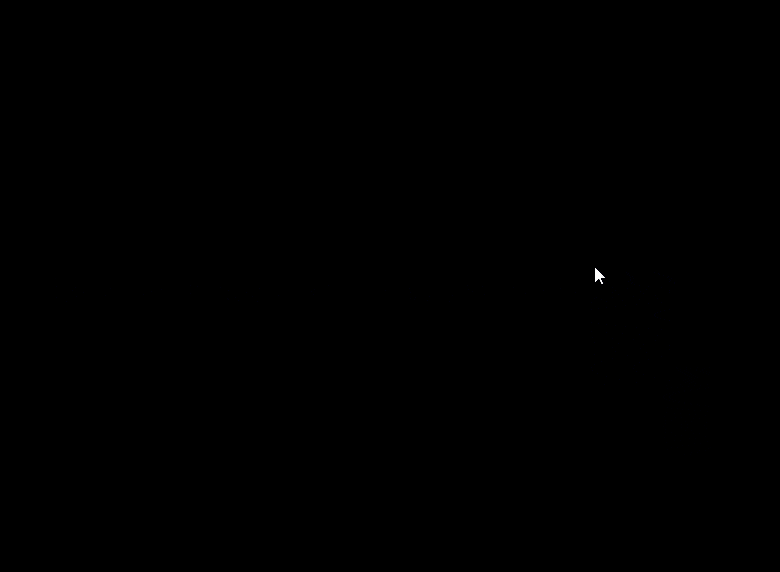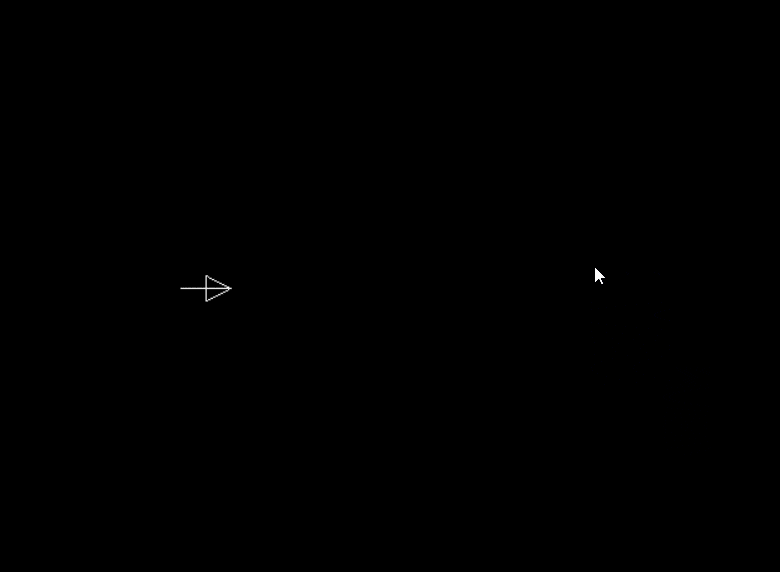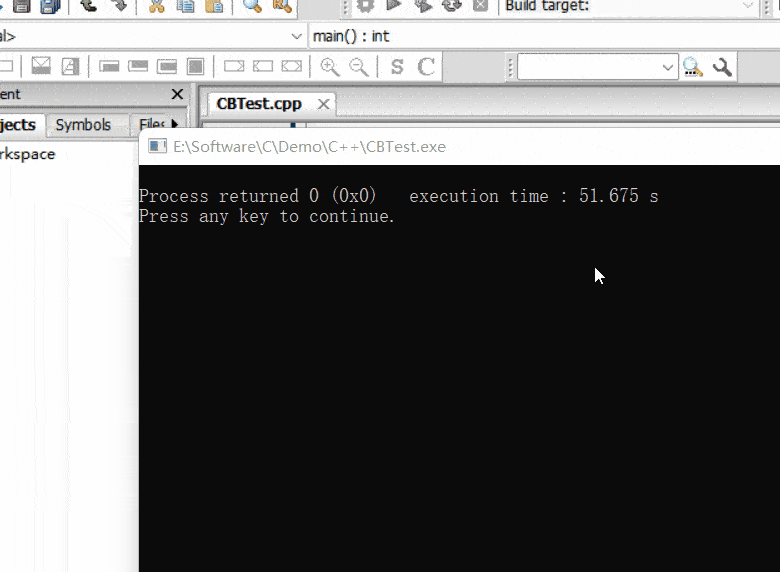
2. initgraph
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void initgraph( int *graphdriver, int *graphmode, char *pathtodriver); |
初始化图形系统 |
参数:
int *graphdriver: 一个指向整数的指针。用于指定要使用的图形驱动程序。图形驱动程序是一组软件代码,负责与特定的图形硬件进行通信。常见的图形驱动程序有 DETECT(自动检测系统中可用的图形硬件并选择合适的驱动程序)、EGAVGA_driver(用于 EGA 或 VGA 显示器)等。int *graphmode:一个指向整数的指针。用于指定要使用的图形模式。不同的图形驱动程序支持多种图形模式,每种模式具有不同的分辨率、颜色深度等特性。如果graphdriver参数设置为 DETECT,则可以将graphmode指针指向的变量初始化为0,让系统自动选择合适的图形模式。char *pathtodriver:一个指向字符的指针。用于指定图形驱动程序文件的路径。图形驱动程序通常以.BGI为扩展名的文件形式存在。如果该参数设置为""(空字符串),则系统会在当前目录下查找图形驱动程序文件。
2.2 演示示例
1 |
|
2.3 运行结果

3. inport
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int inport(int protid); |
从硬件端口中输入,即从指定的 I/O 端口读取一个 16 位(2 字节)的数据 |
参数:
portid:要读取数据的 I/O 端口号。不同的硬件设备会使用不同的端口号,比如,键盘控制器常用的端口号是0x60。在使用inport函数时,需要根据具体的硬件设备和操作需求来确定正确的端口号。
返回值:
从指定 I/O 端口读取到的 16 位数据。若读取过程中出现错误,返回值的具体情况可能因系统和硬件而异。
3.2 演示示例
1 |
|
4. insline
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void insline(void); |
在当前光标位置插入一行空行,原光标所在行及其下方的所有行都会向下移动一行 【在 Turbo C 等早期 C 编译器的图形库或控制台操作库中使用】 |
4.2 演示示例
1 |
|
5. installuserdriver
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int installuserdriver(char *name, int (*detect)(void)); |
安装设备驱动程序到BGI设备驱动程序表中 |
注意: 该函数在 WinBGI 中不可用
5.2 演示示例
1 |
|
6. installuserfont
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int installuserfont( char *name ); |
安装未嵌入BGI系统的字体文件(CHR) |
注意: 该函数在 WinBGI 中不可用
6.2 演示示例
1 |
|
7. int86
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int int86(int intr_num, union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs); |
通用8086软中断接口,用于在 DOS 环境下执行软件中断调用 |
参数:
int intr_num:指定要执行的中断号。在 DOS 系统中,不同的中断号对应着不同的功能。例如,中断号0x10通常用于 BIOS 的视频服务,中断号0x21用于 DOS 系统功能调用。union REGS *inregs:一个指向union REGS联合体的指针,用于传递输入参数到中断服务程序。union REGS联合体包含了多个寄存器的成员,允许你设置不同寄存器的值,以满足特定中断服务的要求。union REGS *outregs:一个指向union REGS联合体的指针。用于接收 DOS 中断服务程序返回的结果。当intdosx函数调用完成后,DOS 中断服务程序会将返回值存储在相应的寄存器中,通过outregs可以获取这些返回值。
union REGS 联合体:
1 | union REGS { |
返回值: 中断服务程序执行的状态。
0表示执行成功。- 非零值表示执行过程中出现错误。具体的错误含义可能因中断号和中断服务程序而异。
7.2 演示示例
1 |
|
8. int86x
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int int86x(int intr_num, union REGS *insegs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs); |
通用8086软中断接口,是一个在 DOS 环境下使用的函数,主要用于执行指定中断号的软件中断。 |
参数:
int intr_num:参考7中所示union REGS *inregs:参考7中所示union REGS *outregs:参考7中所示struct SREGS *segregs: 一个指向struct SREGS结构体的指针。
作用:用于传递和接收段寄存器的值。struct SREGS结构体包含了多个段寄存器成员,如ds、es、ss等。在某些 DOS 功能调用中,可能需要设置或获取段寄存器的值,这时就可以使用segregs参数。
struct SREGS 结构体:
1 | struct SREGS { |
返回值: 中断服务程序执行的状态。
0表示执行成功。- 非零值表示执行过程中出现错误。具体的错误含义可能因中断号和中断服务程序而异。
8.2 演示示例
1 |
|
9. intdos
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int intdos(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs); |
执行一次 DOS 软件中断(通常是中断向量号为 0x21 的中断) |
参数:
union REGS *inregs:一个指向union REGS联合体的指针。用于向 DOS 中断服务程序传递输入参数。union REGS联合体把8位寄存器(如 AH、AL 等)和16位寄存器(如 AX、BX 等)组合在一起,方便开发者设置不同大小的寄存器值。在调用intdos之前,你要依据具体的 DOS 功能需求,把相应的参数存于inregs所指向的联合体中。union REGS *outregs:一个指向union REGS联合体的指针。用于接收 DOS 中断服务程序返回的结果。当intdosx函数调用完成后,DOS 中断服务程序会将返回值存储在相应的寄存器中,通过outregs可以获取这些返回值。
9.2 演示示例
1 |
|
10. intdosx
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int intdosx(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs); |
它主要作用是触发一个 DOS 软件中断(通常是中断号 0x21),并通过寄存器传递参数和获取返回值,从而实现对 DOS 系统功能的调用。 |
参数:
union REGS *inregs:参考 9 中所示union REGS *outregs:参考 9 中所示struct SREGS *segregs: 一个指向struct SREGS结构体的指针。
作用:用于传递和接收段寄存器的值。struct SREGS结构体包含了多个段寄存器成员,如ds、es、ss等。在某些 DOS 功能调用中,可能需要设置或获取段寄存器的值,这时就可以使用segregs参数。
返回值:
DOS 中断调用的状态。通常,返回值为 0 表示调用成功,非零值表示调用过程中出现错误。
10.2 演示示例
1 |
|
11. intr
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void intr(int intr_num, struct REGPACK *preg); |
它是一个在早期 DOS 环境下用于进行软件中断调用的函数 |
参数:
int intr_num:要调用的中断号。在 DOS 和 BIOS 系统中,不同的中断号对应着不同的功能。例如,中断号0x10通常用于 BIOS 的视频服务,中断号0x21用于 DOS 系统功能调用。struct REGPACK *preg:这是一个指向struct REGPACK结构体的指针。struct REGPACK结构体用于存储和传递 CPU 寄存器的值。在调用中断之前,你可以通过该结构体设置输入参数(即设置寄存器的值);中断调用完成后,该结构体中的值会被更新为中断服务程序返回的结果。
1 | struct REGPACK { |
这个结构体包含了多个成员,分别对应不同的 CPU 寄存器。例如:
r_ax对应 AX 寄存器。r_bx对应 BX 寄存器。- 以此类推,
r_cx、r_dx等分别对应 CX、DX 等寄存器。
11.2 演示示例
1 |
|
12. ioctl
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int ioctl(int fd, int cmd, ...) ; |
控制 I/O 设备 |
参数:
fd:文件描述符cmd: 交互协议,设备驱动将根据 cmd 执行对应操作…: 可变参数arg,依赖 cmd 指定长度以及类型
12.2 演示示例
1 |
|
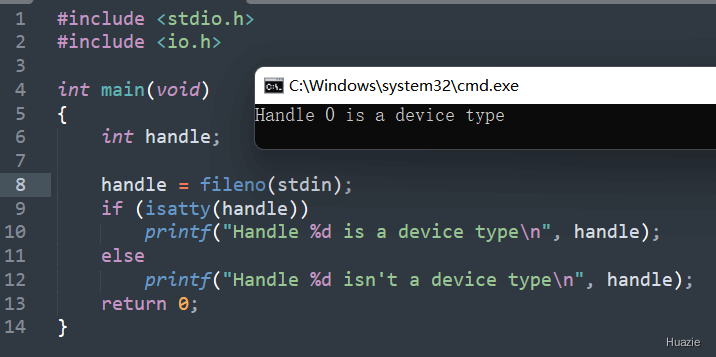
13. isatty
13.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isatty(int handle); |
用于检查给定的文件描述符(file descriptor)是否关联到一个终端设备(teletype,即 TTY) |
它通常用于判断程序是否运行在交互式终端环境中,从而决定是否启用终端相关的功能(如彩色输出、交互式输入等)。
参数:
handle:文件描述符(file descriptor),例如:0(标准输入)、1(标准输出)、2(标准错误)。
13.2 演示示例
1 |
|
13.3 运行结果
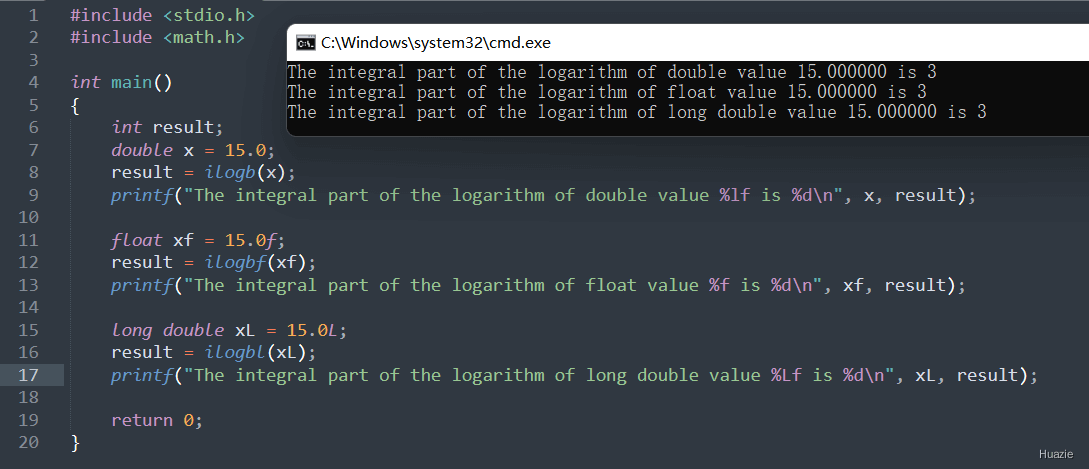
14. ilogb,ilogbf,ilogbfl
14.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int ilogb (double x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(double) |
int ilogbf (float x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(float) |
int ilogbl (long double x); |
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(long double) |
如果计算成功,则返回 x 的对数的整数部分。如果 x 为 0,则此函数返回FP_ILOGB0 并报告错误。如果 x 是NaN值,则此函数返回 FP_ILOGBNAN 并报告错误。如果 x 是正无穷大或负无穷大,此函数将返回 INT_MAX 并报告错误。
14.2 演示示例
1 |
|
14.3 运行结果
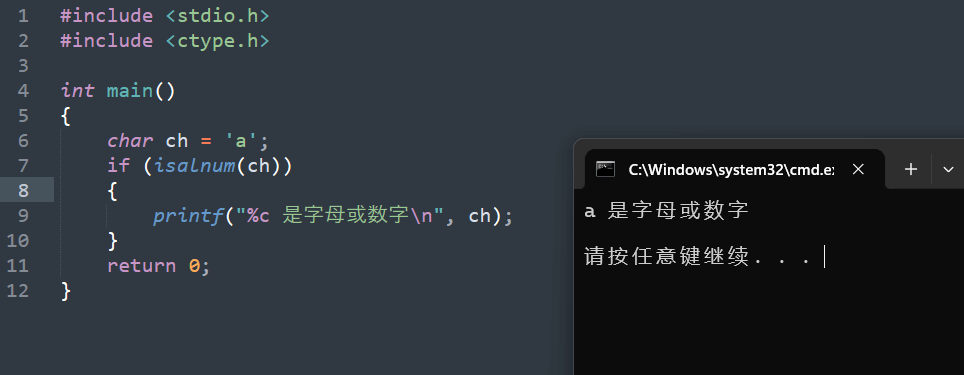
15. isalnum
15.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isalnum(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为字母或数字 |
参数:
c: 待检查的字符
返回值:
- 若字符为字母或数字,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
15.2 演示示例
1 |
|
从上面示例中,我们可以看到 char 类型的 ch 变量传入了 isalnum 函数,而它函数声明中的入参是 int 类型,那这是为什么呢?
这其实同 C 语言的自动类型转换有关。 我们知道在 C 语言中,char 类型本质上是一种整数类型,它占用一个字节(8 位)的存储空间,用于存储字符的 ASCII 码值(或其他字符编码值)。例如,字符 'a' 的 ASCII 码值是 97。当将一个 char 类型的变量作为参数传递给 isalnum 这种期望 int 类型参数的函数时,C 编译器会自动将 char 类型的值提升为 int 类型。这种转换是隐式的,不需要程序员显式地进行类型转换操作。例如,当执行 isalnum('A') 时,字符 'A' 的 ASCII 码值 97 会被自动提升为 int 类型的 97,然后传递给 isalnum 函数进行处理。
15.3 运行结果
16. isalpha
16.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isalpha(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为(大写或小写)字母 |
参数:
c: 待检查的字符
返回值:
- 如果字符是(大写或小写)字母,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
16.2 演示示例
1 |
|
16.3 运行结果
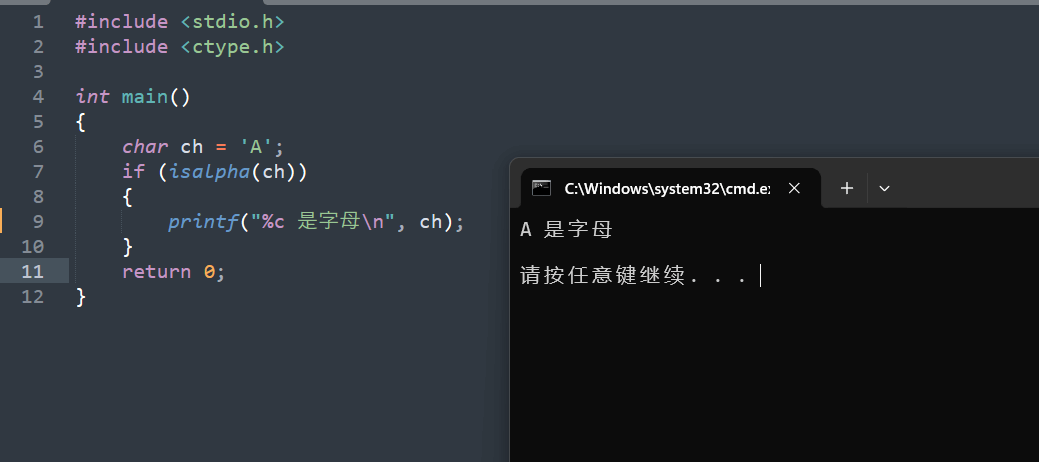
17. isdigit
17.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isdigit(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为数字(0 - 9) |
参数:
c: 待检查的字符
返回值:
- 若字符是数字,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
17.2 演示示例
1 |
|
17.3 运行结果
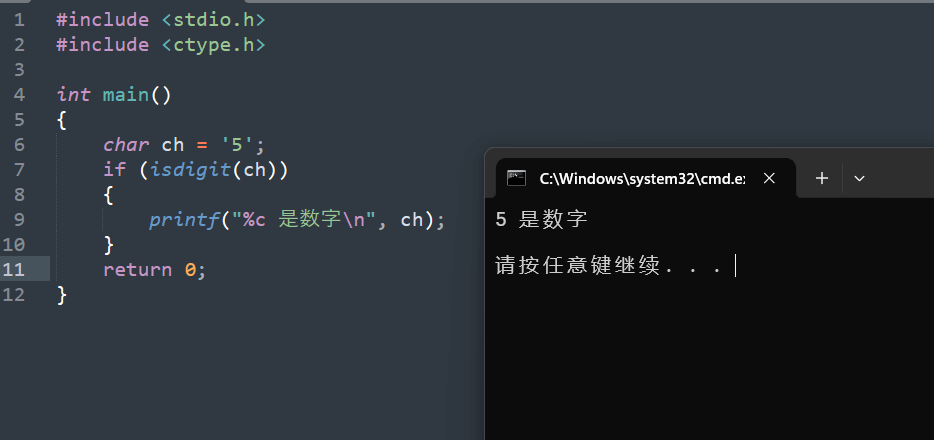
18. isinf
18.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isinf(double x); |
检查浮点数 x 是否为无穷大(正无穷或负无穷) |
参数:
x: 待检查的浮点数
返回值:
- 如果是无穷大,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
18.2 演示示例
1 |
|
18.3 运行结果

19. isnan
19.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isnan(double x); |
检查浮点数 x 是否为非数字(NaN) |
参数:
x: 待检查的浮点数
返回值:
- 如果是 NaN,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
19.2 演示示例
1 |
|
19.3 运行结果

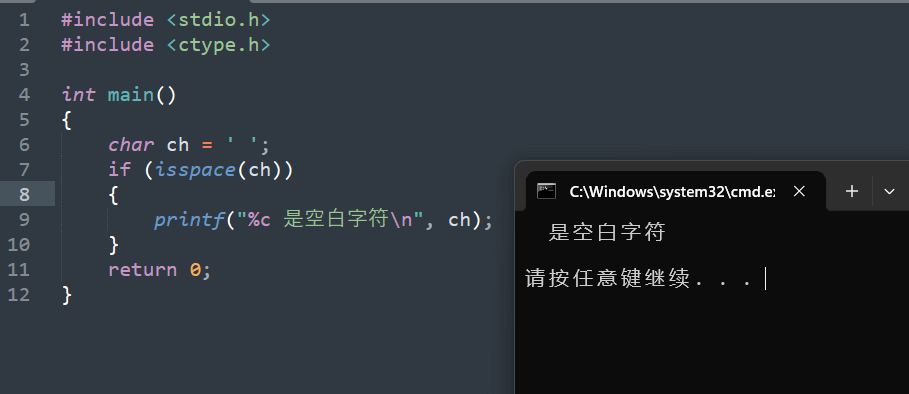
20. isspace
20.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int isspace(int c); |
检查字符 c 是否为空白字符,如空格(’ ‘)、制表符(’\t’)、换行符(’\n’)等。 |
参数:
c: 待检查的字符
返回值:
- 若字符是空白字符,返回非零值;
- 否则返回 0。
20.2 演示示例
1 |
|
20.3 运行结果
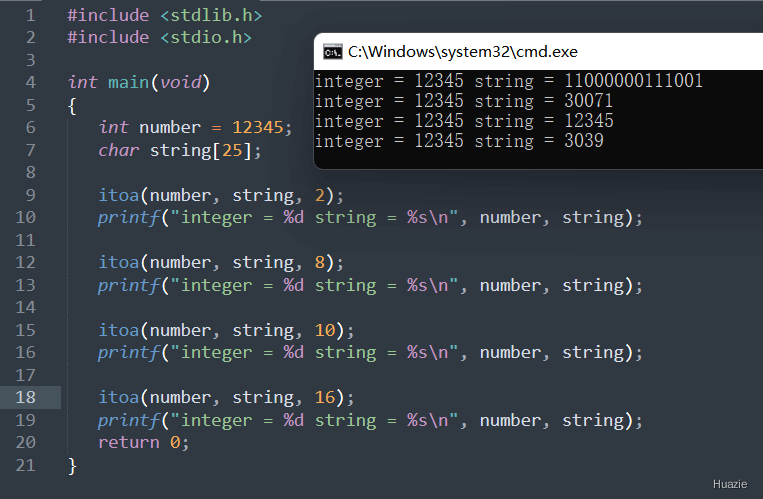
21. itoa
21.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char * itoa(int value, char *string, int radix); |
把一整数转换为字符串 |
参数:
value: 被转换的整数string: 转换后储存的字符数组radix: 转换进制数,如2,8,10,16 进制等,大小应在2-36之间
21.2 演示示例
1 |
|
21.3 运行结果